Some neural circuit models from theoretical neuroscience are already implemented as built-in system classes in the DSN library.
dsn.util.systems
system
system(self, fixed_params, behavior)
Base class for systems using DSN modeling.
Degenerate solution networks (DSNs) learn the full parameter space of models given some model behavioral constraints. Given some system choice and a behavioral specification, these classes are designed to perform the system specific functions that are necessary for training the corresponding DSN.
Attributes
self.D (int): Dimensionality of \(z\).self.num_suff_stats (int): Dimensionality of behavioral constraint vector \(T(x)\).all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.fixed_params (dict): Parameter string indexes its fixed value.free_params (list): List of strings inall_paramsbut notfixed_params.keys(). These params make up z.behavior (dict): Contains the behavioral type and the constraints.mu (np.array): The mean constrain vector for DSN optimization.all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.z_labels (list): List of tex strings for free parameters.T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).density_network_init_mu (np.array): Center of density network gaussian init.density_network_bounds (list): List of np.arrays of lower and upper bounds. None if no bounds.has_support_map (bool): True if there is a support transformation.
get_all_sys_params
system.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_free_params
system.get_free_params(self)
Returns members of all_params not in fixed_params.keys().
Returns
free_params (list): List of strings of parameters in \(z\).
get_z_labels
system.get_z_labels(self)
Returns z_labels.
Returns
z_labels (list): List of tex strings for free parameters.
get_T_x_labels
system.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
compute_suff_stats
system.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
system.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
center_suff_stats_by_mu
system.center_suff_stats_by_mu(self, T_x)
Center sufficient statistics by the mean parameters mu.
Arguments
- T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
- mu (np.array): mean vector of constraints
Returns
T_x_mu_centered (tf.tensor): Mean centered sufficient statistics of samples.
get_behavior_str
system.get_behavior_str(self)
Returns behavior_str.
Returns
behavior_str (str): String for DSN filenaming.
Linear2D
Linear2D(self, fixed_params, behavior)
Linear two-dimensional system.
This is a simple system explored in the DSN tutorial, which demonstrates the utility of DSNs in an intuitive way.
\begin{equation} \tau \dot{x} = Ax, A = \begin{bmatrix} a_1 & a_2 \\ a_3 & a_4 \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
Behaviors:
‘oscillation’ - specify a distribution of oscillatory frequencies
Attributes
behavior (dict): see Linear2D.compute_suff_stats
get_all_sys_params
Linear2D.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
- \(A\) - 2x2 dynamics matrix
- \(\tau\) - scalar timescale parameter
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_T_x_labels
Linear2D.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Behaviors:
‘oscillation’ - \([\)real(\(\lambda_1\)), \(\frac{\text{imag}(\lambda_1)}{2 \pi}\), real\((\lambda_1)^2\), \((\frac{\text{imag}(\lambda_1)}{2 \pi})^2]\)
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
compute_suff_stats
Linear2D.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Behaviors:
‘oscillation’ - Specifies a distribution of oscillatory frequencies and expansion/decay factors using the eigendecomposition of the dynamics matrix. \begin{equation} E_{x\sim p(x \mid z)}\left[T(x)\right] = f_{p,T}(z) = E \begin{bmatrix} \text{real}(\lambda_1) \\ \frac{\text{imag}(\lambda_1)}{2\pi} \\ \text{real}(\lambda_1)^2 \\ (\frac{\text{imag}(\lambda_1)}{2\pi}^2 \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
Linear2D.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
support_mapping
Linear2D.support_mapping(self, inputs)
Maps from real numbers to support of parameters.
Arguments:
inputs (np.array): Input from previous layers of the DSN.
Returns
Z (np.array): Samples from the DSN at the final layer.
STGCircuit
STGCircuit(self, fixed_params, behavior, model_opts={'dt': 0.025, 'T': 200, 'fft_start': 20, 'w': 20})
5-neuron STG circuit from Gutierrez et al. 2013.
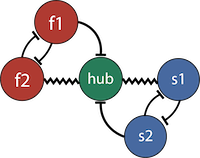
Each neurons membrane potential is the solution of the following differential equation.
\[C_m \frac{\partial V_m}{\partial t} = - \left[ I_{leak} + I_{Ca} + I_K + I_h + I_{elec} + I_{syn}\right]\]The membrane potential of each neuron is a affected by the leak, Calcium, Potassium, hyperpolarization, electrical and synaptic currents, respectively.
The capictance of the circuit is set to \(C_m = 1nF\). All of these fixed parameters at the level of model specification can seemlessly be set as free parameters of a DSN with simple modifications of this system class.
Each current has an associated reversal potential: \(V_{leak} = -40mV\), \(V_{Ca} = 100mV\), \(V_K = -80mV\), \(V_h = -20mV\), and \(V_{syn} = -75mV\). Each current is a function of the difference in membrane and reversal potential multiplied by a conductance:
\[I_{leak} = g_{leak} (V_m - V_{leak})\] \[I_{elec} = g_{el} (V_m^{post} - V_m^{pre})\] \[I_{syn} = g_{syn} S_\infty^{pre} (V_m^{post} - V_{syn})\] \[I_{Ca} = g_{Ca} M_\infty (V_m - V_{Ca})\] \[I_K = g_K N (V_m - V_K)\] \[I_h = g_h H(V_m - V_h)\]where \(g_{el}\) and \(g_{syn}\) are DSN-focused parameters, \(g_{leak} = 1 \times 10^{-4} \mu S\), and \(g_{Ca}\), \(g_{K}\), and \(g_{h}\) have different values based on fast, intermediate (hub) or slow neuron. Fast: \(g_{Ca} = 1.9 \times 10^{-2}\), \(g_K = 3.9 \times 10^{-2}\), and \(g_h = 2.5 \times 10^{-2}\). Intermediate: \(g_{Ca} = 1.7 \times 10^{-2}\), \(g_K = 1.9 \times 10^{-2}\), and \(g_h = 8.0 \times 10^{-3}\). Intermediate: \(g_{Ca} = 8.5 \times 10^{-3}\), \(g_K = 1.5 \times 10^{-2}\), and \(g_h = 1.0 \times 10^{-2}\).
The Calcium, Potassium, and hyperpolarization channels have time-dependent gating dynamics dependent on steady-state gating varibles \(M_\infty\), \(N_\infty\) and \(H_\infty\), respectively.
\[M_{\infty} = 0.5 \left( 1 + \tanh \left( \frac{V_m - v_1}{v_2} \right) \right)\] \[\frac{\partial N}{\partial t} = \lambda_N (N_\infty - N)\] \[N_\infty = 0.5 \left( 1 + \tanh \left( \frac{V_m - v_3}{v_4} \right) \right)\] \[\lambda_N = \phi_N \cosh \left( \frac{V_m - v_3}{2 v_4} \right)\] \[\frac{\partial H}{\partial t} = \frac{\left( H_\infty - H \right)}{\tau_h}\] \[H_\infty = \frac{1}{1 + \exp \left( \frac{V_m + v_5}{v_6} \right)}\] \[\tau_h = 272 - \left( \frac{-1499}{1 + \exp \left( \frac{-V_m + v_7}{v_8} \right)} \right)\]where \(v_1 = 0mV\), \(v_2 = 20mV\), \(v_3 = 0mV\), \(v_4 = 15mV\), \(v_5 = 78.3mV\), \(v_6 = 10.5mV\), \(v_7 = -42.2mV\), \(v_8 = 87.3mV\), \(v_9 = 5mV\), and \(v_{th} = -25mV\).
Finally, there is a synaptic gating variable as well:
\[S_\infty = \frac{1}{1 + \exp \left( \frac{v_{th} - V_m}{v_9} \right)}\]Attributes
behavior (dict): see STGCircuit.compute_suff_stats
get_all_sys_params
STGCircuit.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
- \(g_{el}\) - electrical coupling conductance
- \(g_{synA}\) - synaptic strength A
- \(g_{synB}\) - synaptic strength B
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_T_x_labels
STGCircuit.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Behaviors:
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
filter_Z
STGCircuit.filter_Z(self, z)
Returns the system matrix/vector variables depending free parameter ordering.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
W (tf.tensor): [C,M,4,4] Dynamics matrices.
I (tf.tensor): [T,C,1,4,1] Static inputs.
eta (tf.tensor): [T,C] Inactivations.
simulate
STGCircuit.simulate(self, z, db=False)
Simulate the STG circuit given parameters z.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
g(z) (tf.tensor): Simulated system activity.
compute_suff_stats
STGCircuit.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Behaviors:
‘standard’ -
Add a description.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
simulation_suff_stats
STGCircuit.simulation_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics that require simulation.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Simulation-derived sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
STGCircuit.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
support_mapping
STGCircuit.support_mapping(self, inputs)
Maps from real numbers to support of parameters.
Arguments:
inputs (np.array): Input from previous layers of the DSN.
Returns
Z (np.array): Samples from the DSN at the final layer.
V1Circuit
V1Circuit(self, fixed_params, behavior, model_opts={'g_FF': 'c', 'g_LAT': 'linear', 'g_RUN': 'r'}, T=100, dt=0.02, init_conds=array([[1.00506511],
[1.00599704],
[1.01756709],
[1.0027543 ]]))
4-neuron V1 circuit.
This is the standard 4-neuron rate model of V1 activity consisting of
- E: pyramidal (excitatory) neurons
- P: parvalbumim expressing inhibitory neurons
- S: somatostatin expressing inhibitory neurons
- V: vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) expressing inhibitory neurons
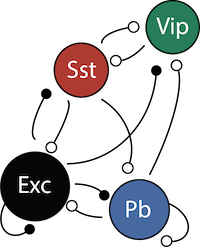
The dynamics of each neural populations average rate \(r = \begin{bmatrix} r_E \\ r_P \\ r_S \\ r_V \end{bmatrix}\) are given by: \begin{equation} \tau \frac{dr}{dt} = -r + [Wr + h]_+^n \end{equation}
Attributes
behavior (dict): see V1Circuit.compute_suff_statsmodel_opts (dict):- model_opts[
'g_FF']'c'(default) \(g_{FF}(c) = c\)'saturate'\(g_{FF}(c) = \frac{c^a}{c_{50}^a + c^a}\)
- model_opts[
'g_LAT']'linear'(default) \(g_{LAT}(c,s) = c[s - s_0]_+\)'square'\(g_{LAT}(c,s) = c[s^2 - s_0^2]_+\)
- model_opts[
'g_RUN']'r'(default) \(g_{RUN}(r) = r\)
- model_opts[
T (int): Number of simulation time points.dt (float): Time resolution of simulation.init_conds (list): Specifies the initial state of the system.
get_all_sys_params
V1Circuit.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
- \(W_{EE}\) - strength of excitatory-to-excitatory projection
- \(W_{XE}\) - strength of excitatory-to-VIP projection
- \(W_{EP}\) - strength of parvalbumin-to-excitatory projection
- \(W_{PP}\) - strength of parvalbumin-to-parvalbumin projection
- \(W_{VP}\) - strength of parvalbumin-to-VIP projection
- \(W_{ES}\) - strength of somatostatin-to-excitatory projection
- \(W_{PS}\) - strength of somatostatin-to-parvalbumin projection
- \(W_{VS}\) - strength of somatostatin-to-VIP projection
- \(W_{SV}\) - strength of VIP-to-somatostatin projection
- \(b_{E}\) - constant input to excitatory population
- \(b_{P}\) - constant input to parvalbumin population
- \(b_{S}\) - constant input to somatostatin population
- \(b_{V}\) - constant input to VIP population
- \(h_{FF,E}\) - feed-forward input to excitatory population
- \(h_{FF,P}\) - feed-forward input to parvalbumin population
- \(h_{LAT,E}\) - lateral input to excitatory population
- \(h_{LAT,P}\) - lateral input to parvalbumin population
- \(h_{LAT,S}\) - lateral input to somatostatin population
- \(h_{LAT,V}\) - lateral input to VIP population
- \(h_{RUN,E}\) - locomotion input to excitatory population
- \(h_{RUN,P}\) - locomotion input to parvalbumin population
- \(h_{RUN,S}\) - locomotion input to somatostatin population
- \(h_{RUN,V}\) - locomotion input to VIP population
- \(\tau\) - dynamics timescale
- \(n\) - scalar for power of dynamics
- \(s_0\) - reference stimulus level
When model_opts['g_FF'] == 'saturate'
- \(a\) - contrast saturation shape
- \(c_{50}\) - constrast at 50%
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_T_x_labels
V1Circuit.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Behaviors:
‘old_difference’ - \([d_{E,ss}, d_{P,ss}, d_{S,ss}, d_{V,ss}, d_{E,ss}^2, d_{P,ss}^2, d_{S,ss}^2, d_{V,ss}^2]\)
‘difference’ - \([r_{E,ss}(c,s,r), ..., r_{E,ss}(c,s,r)^2, ...]\)
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
filter_Z
V1Circuit.filter_Z(self, z)
Returns the system matrix/vector variables depending free parameter ordering.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
W (tf.tensor): [C,M,4,4] Dynamics matrices.
b (tf.tensor): [1,M,4,1] Static inputs.
h_FF (tf.tensor): [1,M,4,1] Feed forward inputs.
h_LAT (tf.tensor): [1,M,4,1] Lateral inputs.
h_RUN (tf.tensor): [1,M,4,1] Running inputs.
tau (tf.tensor): [C,M,1,1] Dynamics timescales.
n (tf.tensor): [C,M,1,1] Dynamics power coefficients.
s_0 (tf.tensor): [1,M,1,1] Reference stimulus values.
a (tf.tensor): [1,M,1,1] Contrast saturation shape.
c_50 (tf.tensor): [1,M,1,1] Contrast at 50%.
simulate
V1Circuit.simulate(self, z)
Simulate the V1 4-neuron circuit given parameters z.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
g(z) (tf.tensor): Simulated system activity.
compute_suff_stats
V1Circuit.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Behaviors:
‘difference’ -
The total number of conditions from all of self,behavior.c_vals, s_vals, and r_vals should be two. The steady state of the first condition \((c_1,s_1,r_1)\) is subtracted from that of the second condition \((c_2,s_2,r_2)\) to get a difference vector \begin{equation} d_{\alpha,ss} = r_{\alpha,ss}(c_2,s_2,r_2) - r_{\alpha,ss}(c_1,s_1,r_1) \end{equation}
The total constraint vector is \begin{equation} E_{x\sim p(x \mid z)}\left[T(x)\right] = \begin{bmatrix} d_{E,ss} \\ d_{P,ss} \\ d_{S,ss} \\ d_{V,ss} \\ d_{E,ss}^2 \\ d_{P,ss}^2 \\ d_{S,ss}^2 \\ d_{V,ss}^2 \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
‘data’ -
The user specifies the grid inputs for conditions via self.behavior.c_vals, s_vals, and r_vals. The first and second moments of the steady states for these conditions make up the sufficient statistics vector. Since the index is \((c,s,r)\), values of r are iterated over first, then s, then c (as is the c-standard) to construct the \(T(x)\) vector.
The total constraint vector is \begin{equation} E_{x\sim p(x \mid z)}\left[T(x)\right] = \begin{bmatrix} r_{E,ss}(c,s,r) \\ … \\ r_{E,ss}(c,s,r)^2 \\ … \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
simulation_suff_stats
V1Circuit.simulation_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics that require simulation.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Simulation-derived sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
V1Circuit.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
support_mapping
V1Circuit.support_mapping(self, inputs)
Maps from real numbers to support of parameters.
Arguments:
inputs (np.array): Input from previous layers of the DSN.
Returns
Z (np.array): Samples from the DSN at the final layer.
get_behavior_str
V1Circuit.get_behavior_str(self)
Returns behavior_str.
Returns
behavior_str (str): String for DSN filenaming.
SCCircuit
SCCircuit(self, fixed_params, behavior, model_opts={'params': 'reduced', 'C': 1, 'N': 100})
4-neuron SC circuit from Duan et al. 2018.
This is a 4-neuron rate model of SC activity across two hemispheres
- LP: Left, Pro
- LA: Left, Anti
- RA: Right, Anti
- RP: Right, Pro
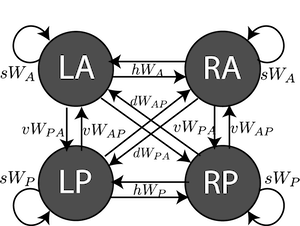
Attributes
behavior (dict): see SCCircuit.compute_suff_stats
get_all_sys_params
SCCircuit.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
- \(sW\) - strength of self connections
- \(vW\) - strength of vertical connections
- \(dW\) - strength of diagonal connections
- \(hW\) - strength of horizontal connections
- \(E_constant\) - constant input
- \(E_Pbias\) - bias input to Pro units
- \(E_Prule\) - input to Pro units in Pro condition
- \(E_Arule\) - input to Anti units in Anti condition
- \(E_choice\) - input during choice period
- \(E_light\) - input due to light stimulus
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_T_x_labels
SCCircuit.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Behaviors:
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
filter_Z
SCCircuit.filter_Z(self, z)
Returns the system matrix/vector variables depending free parameter ordering.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
W (tf.tensor): [C,M,4,4] Dynamics matrices.
I (tf.tensor): [T,C,1,4,1] Static inputs.
eta (tf.tensor): [T,C] Inactivations.
simulate
SCCircuit.simulate(self, z)
Simulate the V1 4-neuron circuit given parameters z.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
g(z) (tf.tensor): Simulated system activity.
compute_suff_stats
SCCircuit.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Behaviors:
‘standard’ -
Add a description.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
simulation_suff_stats
SCCircuit.simulation_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics that require simulation.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Simulation-derived sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
SCCircuit.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
LowRankRNN
LowRankRNN(self, fixed_params, behavior, model_opts={'rank': 1, 'input_type': 'spont'}, solve_its=25, solve_eps=0.8)
Recent work by (Mastrogiusseppe & Ostojic, 2018) allows us to derive statistical properties of the behavior of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) given a low-rank parameterization of their connectivity. This work builds on dynamic mean field theory (DMFT) for neural networks (Sompolinsky et al. 1988), which is exact in the limit of infinite neurons, but has been shown to yield accurate approximations for finite size networks.
The network model is
\[\dot{x}_i(t) = -x_i(t) + \sum_{j=1}^N J_{ij} \phi(x_j(t)) + I_i\]where the connectivity is comprised of a random and structured component:
\[J_{ij} = g \chi_{ij} + P_{ij}\]The random all-to-all component has elements drawn from \(\chi_{ij} \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \frac{1}{N})\), and the structured component is a sum of \(r\) unit rank terms:
\[P_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^r \frac{m_i^{(k)}n_j^{(k)}}{N}\]The nonlinearity \(\phi\) is set to \(tanh\) in this software, but the theory is general for many other activation functions.
Attributes
behavior (dict): see LowRankRNN.compute_suff_statsmodel_opts (dict):- model_opts[
'rank']1(default) Rank 1 network2
- model_opts[
'input_type']'spont'(default) No input.'gaussian'(default) Gaussian input.
- model_opts[
solve_its (int): Number of langevin dynamics simulation steps.solve_eps (float): Langevin dynamics solver step-size.
get_all_sys_params
LowRankRNN.get_all_sys_params(self)
Returns ordered list of all system parameters and individual element labels.
When model_opts['rank'] == 1
- \(g\) - strength of the random matrix component
- \(M_m\) - mean value of right connectivity vector
- \(M_n\) - mean value of left connectivity vector
- \(\Sigma_m\) - variance of values in right connectivity vector
When model_opts['rank'] == 2
- TODO
Returns
all_params (list): List of strings of all parameters of full system model.
all_param_labels (list): List of tex strings for all parameters.
get_T_x_labels
LowRankRNN.get_T_x_labels(self)
Returns T_x_labels.
Behaviors:
‘struct_chaos’ - \([\mu, \Delta_{\infty}, (\Delta_0 - \Delta_{\infty}), \mu^2, \Delta_{\infty}^2, (\Delta_0 - \Delta_{\infty})^2]\)
Returns
T_x_labels (list): List of tex strings for elements of \(T(x)\).
filter_Z
LowRankRNN.filter_Z(self, z)
Returns the system matrix/vector variables depending free parameter ordering.
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
g (tf.tensor): [1,M] Strength of the random matrix component.
Mm (tf.tensor): [1,M] Mean value of right connectivity vector.
Mn (tf.tensor): [1,M] Mean value of left connectivity vector.
Sm (tf.tensor): [1,M] Variance of values in right connectivity vector.
compute_suff_stats
LowRankRNN.compute_suff_stats(self, z)
Compute sufficient statistics of density network samples.
Behaviors:
‘struct_chaos’ -
When model_opts['rank'] == 1 and model_opts['input_type'] == 'spont'
Set constraints on the mean unit activity \(\mu\), the static variance \(\Delta_{\infty}\), and the temporal variance \(\Delta_T = \Delta_0 - \Delta_{\infty}\). \(\mu\), \(\Delta_0\), and \(\Delta_{\infty}\) can be found for a rank-1 no-input network by solving the following consistency equations.
\[\mu = F(\mu, \Delta_0, \Delta_\infty) = M_m M_n \int \mathcal{D}z \phi(\mu + \sqrt{\Delta_0} z)\]\(\Delta_0 = G(\mu, \Delta_0, \Delta_\infty) = [\Delta_\infty^2 + 2g^2\{\int \mathcal{D}z \Phi^2(\mu + \sqrt{\Delta_0}z) - \int \mathcal{D}z [\int \mathcal{D}x \Phi(\mu + \sqrt{\Delta_0 - \Delta_\infty}x\) \(+ \sqrt{\Delta_\infty}z)]^2\} +M_n^2 \Sigma_m^2 \langle[\phi_i]\rangle^2(\Delta_0 - \Delta_\infty)]^{\frac{1}{2}}\)
\[\Delta_\infty = H(\mu, \Delta_0, \Delta_\infty) = g^2 \int \mathcal{D}z \left[ \int \mathcal{D}x \Phi(\mu + \sqrt{\Delta_0 - \Delta_\infty} + \sqrt{\Delta_\infty}z \right]^2 + M_n^2 \Sigma_m^2 \langle [\phi_i] \rangle^2\]The solutions are found via a Langevin dynamics simulation with step size
self.solve_eps and number of iterations self.solve_its.
The total constraint vector is \begin{equation} E_{x\sim p(x \mid z)}\left[T(x)\right] = \begin{bmatrix} \mu \\ \Delta_\infty \\ \Delta_0 - \Delta_\infty \\ \mu \\ \Delta_\infty^2 \\ (\Delta_0 - \Delta_\infty)^2 \end{bmatrix} \end{equation}
Arguments
- z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
T_x (tf.tensor): Sufficient statistics of samples.
compute_mu
LowRankRNN.compute_mu(self)
Calculate expected moment constraints given system paramterization.
Returns
mu (np.array): Expected moment constraints.
support_mapping
LowRankRNN.support_mapping(self, inputs)
Maps from real numbers to support of parameters.
Arguments:
inputs (np.array): Input from previous layers of the DSN.
Returns
Z (np.array): Samples from the DSN at the final layer.
get_warm_start_inits
LowRankRNN.get_warm_start_inits(self, z)
Calculates warm start initialization for parameter sample.
Arguments:
z (tf.tensor): Density network system parameter samples.
Returns
inits (list): list of (M,) tf.tensor solver inits
References
Dipoppa, Mario, et al. Vision and locomotion shape the interactions between neuron types in mouse visual cortex. Neuron 98.3 (2018): 602-615.
Duan, Chunyu A., et al. Collicular circuits for flexible sensorimotor routing. bioRxiv (2018): 245613.
Gutierrez, Gabrielle J., Timothy O’Leary, and Eve Marder. Multiple mechanisms switch an electrically coupled, synaptically inhibited neuron between competing rhythmic oscillators. Neuron 77.5 (2013): 845-858.
Mastrogiuseppe, Francesca, and Srdjan Ostojic. Linking connectivity, dynamics, and computations in low-rank recurrent neural networks. Neuron 99.3 (2018): 609-623.